Abstract
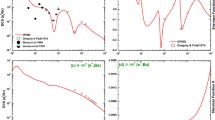
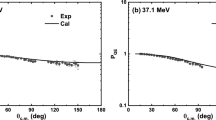
The observation of refractive effects in 16O+16O and 16O+12C elastic scattering data has definitively established the fact that the optical potential for some light heavy-ion systems is relatively transparent and that its real part is deep. Most of the interpretations of the rainbow features of these data rely on the so-called nearside-farside decomposition of the scattering amplitude. Starting from recent optical model analyses of 16O+16O and 16O+12C elastic scattering around 100 MeV incident energy as an example, we present an alternative interpretation based on the barrier-wave/internal-wave decomposition first proposed by Brink and Takigawa. This method, which complements the nearside-farside approach, demonstrates clearly the exceptional transparency of the 16O+16O, and to a lesser extent 16O+12C, interactions at the investigated energies and makes possible the extraction of the two contributions whose interference explains the Airy oscillations seen in the farside amplitude.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. E. Brandan and G. R. Satchler, Phys. Rep. 285, 143 (1997).
M. S. Hussein and K. W. McVoy, Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 12, 103 (1984).
M. E. Brandan, M. S. Hussein, K. W. McVoy, et al., Comments Nucl. Part. Phys. 22, 77 (1996).
M. P. Nicoli, F. Haas, R. M. Freeman, et al., Phys. Rev. C 60, 064608 (1999).
Dao T. Khoa, W. von Oertzen, H. G. Bohlen, et al., Nucl. Phys. A 672, 387 (2000).
A. A. Ogloblin, D. T. Khoa, Y. Kondō, et al., Phys. Rev. C 57, 1797 (1998).
M. P. Nicoli, F. Haas, R. M. Freeman, et al., Phys. Rev. C 61, 034609 (2000).
D. M. Brink, Semi-Classical Methods for Nucleus-Nucleus Scattering (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1985).
R. C. Fuller, Phys. Rev. C 12, 1561 (1975).
Y. Kondō, Y. Sugiyama, Y. Tomita, et al., Phys. Lett. B 365, 17 (1996).
M. L. Halbert, C. B. Fulmer, S. Raman, et al., Phys. Lett. B 51B, 341 (1974).
N. Rowley, H. Doubre, and C. Marty, Phys. Lett. B 69B, 147 (1977).
K. W. McVoy, H. M. Khalil, M. M. Shalaby, et al., Nucl. Phys. A 455, 118 (1986).
K. W. McVoy and M. E. Brandan, Nucl. Phys. A 542, 295 (1992).
D. M. Brink and N. Takigawa, Nucl. Phys. A 279, 159 (1977).
F. Michel, S. Ohkubo, and G. Reidemeister, Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl., No. 132, 7 (1998).
J. Albiński and F. Michel, Phys. Rev. C 25, 213 (1982).
H. M. Khalil, K. W. McVoy, and M. M. Shalaby, Nucl. Phys. A 455, 100 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
From Yadernaya Fizika, Vol. 65, No. 4, 2002, pp. 706–709.
Original English Text Copyright © 2002 by Michel, Brau, Reidemeister, Ohkubo.
This article was submitted by the authors in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michel, F., Brau, F., Reidemeister, G. et al. Interpretation of airy minima in 16O+16O and 16O+12C elastic scattering in terms of a barrier-wave/internal-wave decomposition. Phys. Atom. Nuclei 65, 674–677 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1134/1.1471272
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/1.1471272